1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
| /*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2023, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2023-10-28 Wangyuqiang first version
*/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels
#define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels
// Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins)
// The pins for I2C are defined by the Wire-library.
// On an arduino UNO: A4(SDA), A5(SCL)
// On an arduino MEGA 2560: 20(SDA), 21(SCL)
// On an arduino LEONARDO: 2(SDA), 3(SCL), ...
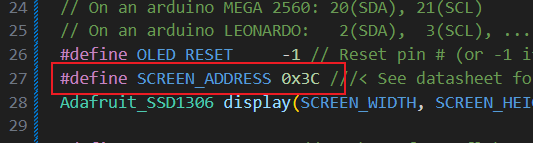
#define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin)
#define SCREEN_ADDRESS 0x3C ///< See datasheet for Address; 0x3D for 128x64, 0x3C for 128x32
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET);
#define NUMFLAKES 10 // Number of snowflakes in the animation example
#define LOGO_HEIGHT 16
#define LOGO_WIDTH 16
static const unsigned char PROGMEM logo_bmp[] =
{ 0b00000000, 0b11000000,
0b00000001, 0b11000000,
0b00000001, 0b11000000,
0b00000011, 0b11100000,
0b11110011, 0b11100000,
0b11111110, 0b11111000,
0b01111110, 0b11111111,
0b00110011, 0b10011111,
0b00011111, 0b11111100,
0b00001101, 0b01110000,
0b00011011, 0b10100000,
0b00111111, 0b11100000,
0b00111111, 0b11110000,
0b01111100, 0b11110000,
0b01110000, 0b01110000,
0b00000000, 0b00110000 };
void testdrawline(); // Draw many lines
void testdrawrect(void); // Draw rectangles (outlines)
void testfillrect(void); // Draw rectangles (filled)
void testdrawcircle(void); // Draw circles (outlines)
void testfillcircle(void); // Draw circles (filled)
void testdrawroundrect(void); // Draw rounded rectangles (outlines)
void testfillroundrect(void); // Draw rounded rectangles (filled)
void testdrawtriangle(void); // Draw triangles (outlines)
void testfilltriangle(void); // Draw triangles (filled)
void testdrawchar(void); // Draw characters of the default font
void testdrawstyles(void); // Draw 'stylized' characters
void testscrolltext(void); // Draw scrolling text
void testdrawbitmap(void); // Draw a small bitmap image
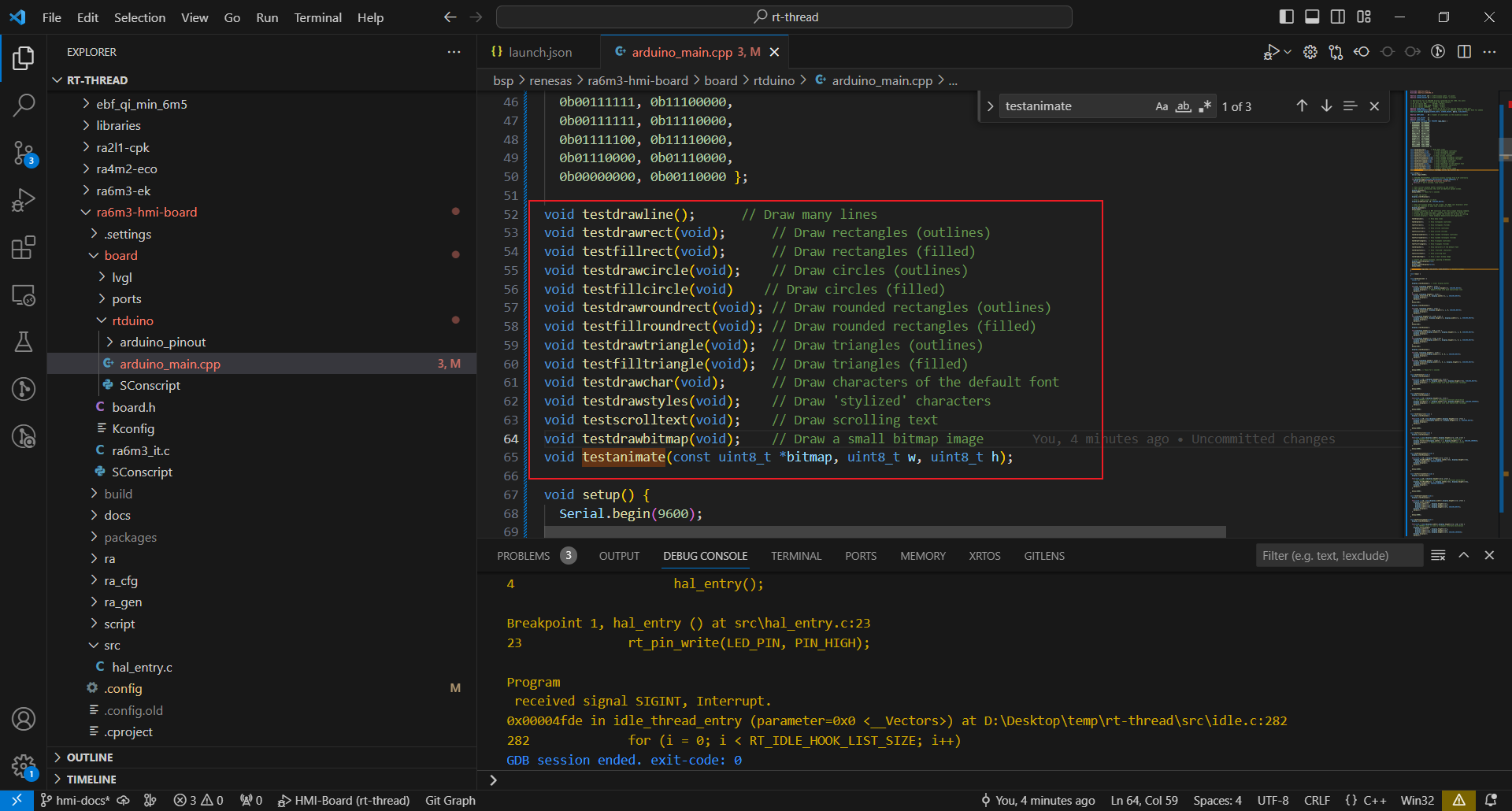
void testanimate(const uint8_t *bitmap, uint8_t w, uint8_t h);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC = generate display voltage from 3.3V internally
if(!display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, SCREEN_ADDRESS)) {
Serial.println(F("SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for(;;); // Don't proceed, loop forever
}
// Show initial display buffer contents on the screen --
// the library initializes this with an Adafruit splash screen.
display.display();
delay(2000); // Pause for 2 seconds
// Clear the buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Draw a single pixel in white
display.drawPixel(10, 10, SSD1306_WHITE);
// Show the display buffer on the screen. You MUST call display() after
// drawing commands to make them visible on screen!
display.display();
delay(2000);
// display.display() is NOT necessary after every single drawing command,
// unless that's what you want...rather, you can batch up a bunch of
// drawing operations and then update the screen all at once by calling
// display.display(). These examples demonstrate both approaches...
testdrawline(); // Draw many lines
testdrawrect(); // Draw rectangles (outlines)
testfillrect(); // Draw rectangles (filled)
testdrawcircle(); // Draw circles (outlines)
testfillcircle(); // Draw circles (filled)
testdrawroundrect(); // Draw rounded rectangles (outlines)
testfillroundrect(); // Draw rounded rectangles (filled)
testdrawtriangle(); // Draw triangles (outlines)
testfilltriangle(); // Draw triangles (filled)
testdrawchar(); // Draw characters of the default font
testdrawstyles(); // Draw 'stylized' characters
testscrolltext(); // Draw scrolling text
testdrawbitmap(); // Draw a small bitmap image
// Invert and restore display, pausing in-between
display.invertDisplay(true);
delay(1000);
display.invertDisplay(false);
delay(1000);
testanimate(logo_bmp, LOGO_WIDTH, LOGO_HEIGHT); // Animate bitmaps
}
void loop() {
}
void testdrawline() {
int16_t i;
display.clearDisplay(); // Clear display buffer
for(i=0; i<display.width(); i+=4) {
display.drawLine(0, 0, i, display.height()-1, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display(); // Update screen with each newly-drawn line
delay(1);
}
for(i=0; i<display.height(); i+=4) {
display.drawLine(0, 0, display.width()-1, i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(250);
display.clearDisplay();
for(i=0; i<display.width(); i+=4) {
display.drawLine(0, display.height()-1, i, 0, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
for(i=display.height()-1; i>=0; i-=4) {
display.drawLine(0, display.height()-1, display.width()-1, i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(250);
display.clearDisplay();
for(i=display.width()-1; i>=0; i-=4) {
display.drawLine(display.width()-1, display.height()-1, i, 0, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
for(i=display.height()-1; i>=0; i-=4) {
display.drawLine(display.width()-1, display.height()-1, 0, i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(250);
display.clearDisplay();
for(i=0; i<display.height(); i+=4) {
display.drawLine(display.width()-1, 0, 0, i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
for(i=0; i<display.width(); i+=4) {
display.drawLine(display.width()-1, 0, i, display.height()-1, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000); // Pause for 2 seconds
}
void testdrawrect(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<display.height()/2; i+=2) {
display.drawRect(i, i, display.width()-2*i, display.height()-2*i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display(); // Update screen with each newly-drawn rectangle
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testfillrect(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<display.height()/2; i+=3) {
// The INVERSE color is used so rectangles alternate white/black
display.fillRect(i, i, display.width()-i*2, display.height()-i*2, SSD1306_INVERSE);
display.display(); // Update screen with each newly-drawn rectangle
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testdrawcircle(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<max(display.width(),display.height())/2; i+=2) {
display.drawCircle(display.width()/2, display.height()/2, i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testfillcircle(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=max(display.width(),display.height())/2; i>0; i-=3) {
// The INVERSE color is used so circles alternate white/black
display.fillCircle(display.width() / 2, display.height() / 2, i, SSD1306_INVERSE);
display.display(); // Update screen with each newly-drawn circle
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testdrawroundrect(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<display.height()/2-2; i+=2) {
display.drawRoundRect(i, i, display.width()-2*i, display.height()-2*i,
display.height()/4, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testfillroundrect(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<display.height()/2-2; i+=2) {
// The INVERSE color is used so round-rects alternate white/black
display.fillRoundRect(i, i, display.width()-2*i, display.height()-2*i,
display.height()/4, SSD1306_INVERSE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testdrawtriangle(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=0; i<max(display.width(),display.height())/2; i+=5) {
display.drawTriangle(
display.width()/2 , display.height()/2-i,
display.width()/2-i, display.height()/2+i,
display.width()/2+i, display.height()/2+i, SSD1306_WHITE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testfilltriangle(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
for(int16_t i=max(display.width(),display.height())/2; i>0; i-=5) {
// The INVERSE color is used so triangles alternate white/black
display.fillTriangle(
display.width()/2 , display.height()/2-i,
display.width()/2-i, display.height()/2+i,
display.width()/2+i, display.height()/2+i, SSD1306_INVERSE);
display.display();
delay(1);
}
delay(2000);
}
void testdrawchar(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextSize(1); // Normal 1:1 pixel scale
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE); // Draw white text
display.setCursor(0, 0); // Start at top-left corner
display.cp437(true); // Use full 256 char 'Code Page 437' font
// Not all the characters will fit on the display. This is normal.
// Library will draw what it can and the rest will be clipped.
for(int16_t i=0; i<256; i++) {
if(i == '\n') display.write(' ');
else display.write(i);
}
display.display();
delay(2000);
}
void testdrawstyles(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextSize(1); // Normal 1:1 pixel scale
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE); // Draw white text
display.setCursor(0,0); // Start at top-left corner
display.println(F("Hello, world!"));
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_BLACK, SSD1306_WHITE); // Draw 'inverse' text
display.println(3.141592);
display.setTextSize(2); // Draw 2X-scale text
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
display.print(F("0x")); display.println(0xDEADBEEF, HEX);
display.display();
delay(2000);
}
void testscrolltext(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
display.setTextSize(2); // Draw 2X-scale text
display.setTextColor(SSD1306_WHITE);
display.setCursor(10, 0);
display.println(F("scroll"));
display.display(); // Show initial text
delay(100);
// Scroll in various directions, pausing in-between:
display.startscrollright(0x00, 0x0F);
delay(2000);
display.stopscroll();
delay(1000);
display.startscrollleft(0x00, 0x0F);
delay(2000);
display.stopscroll();
delay(1000);
display.startscrolldiagright(0x00, 0x07);
delay(2000);
display.startscrolldiagleft(0x00, 0x07);
delay(2000);
display.stopscroll();
delay(1000);
}
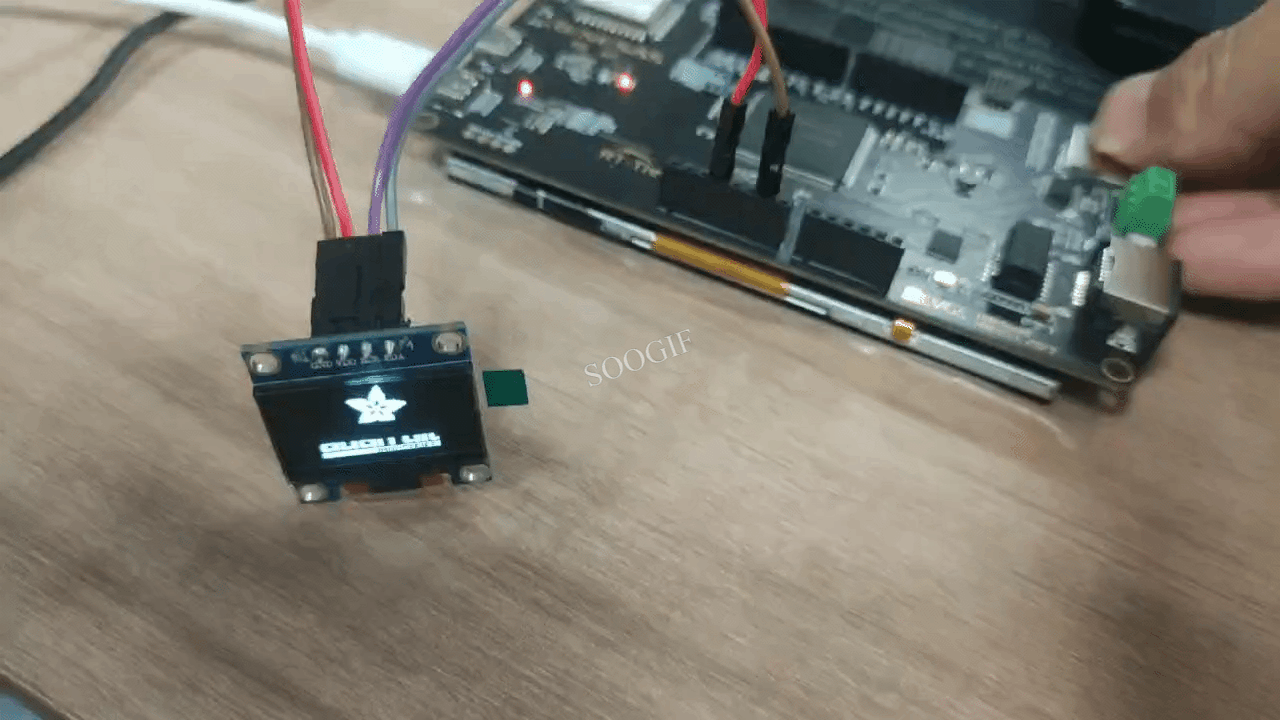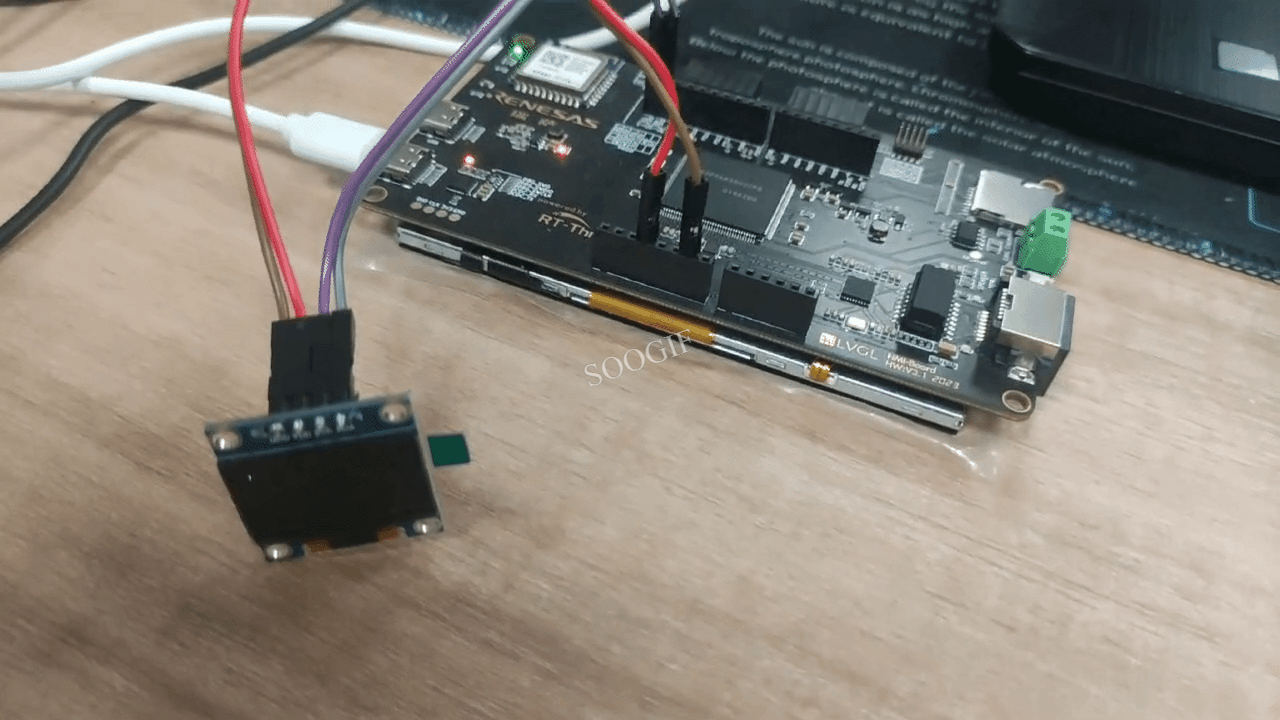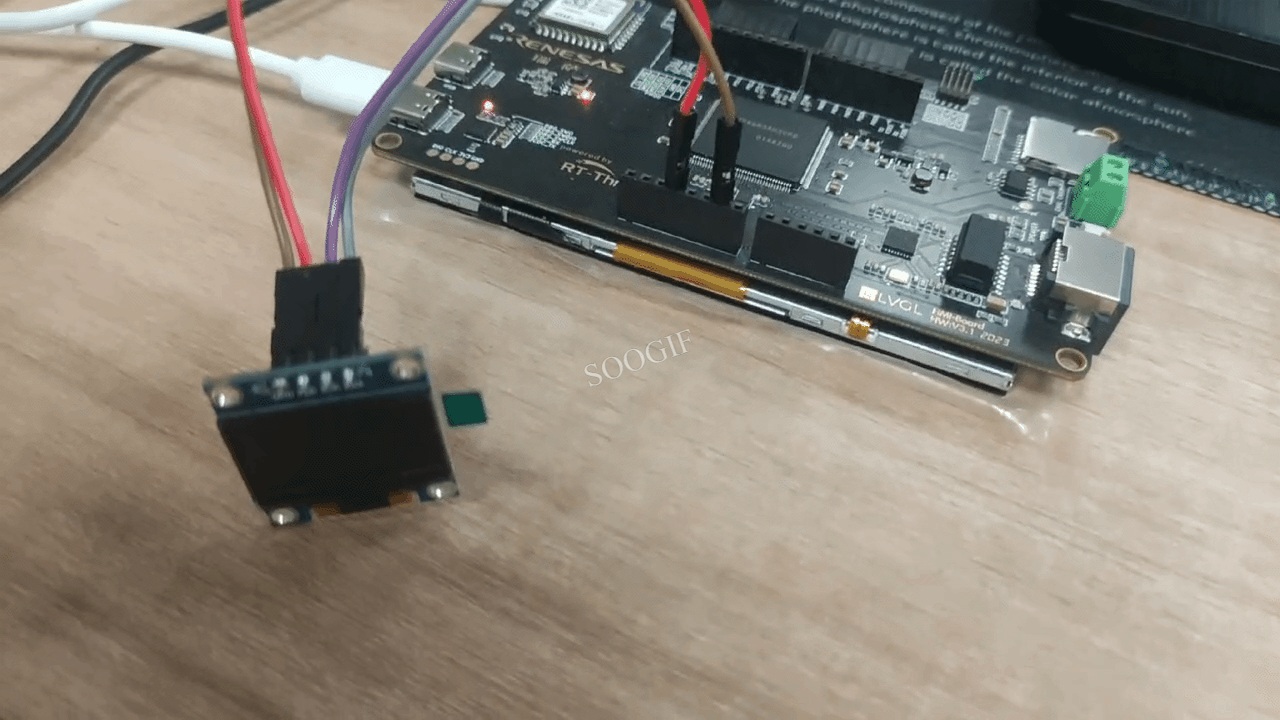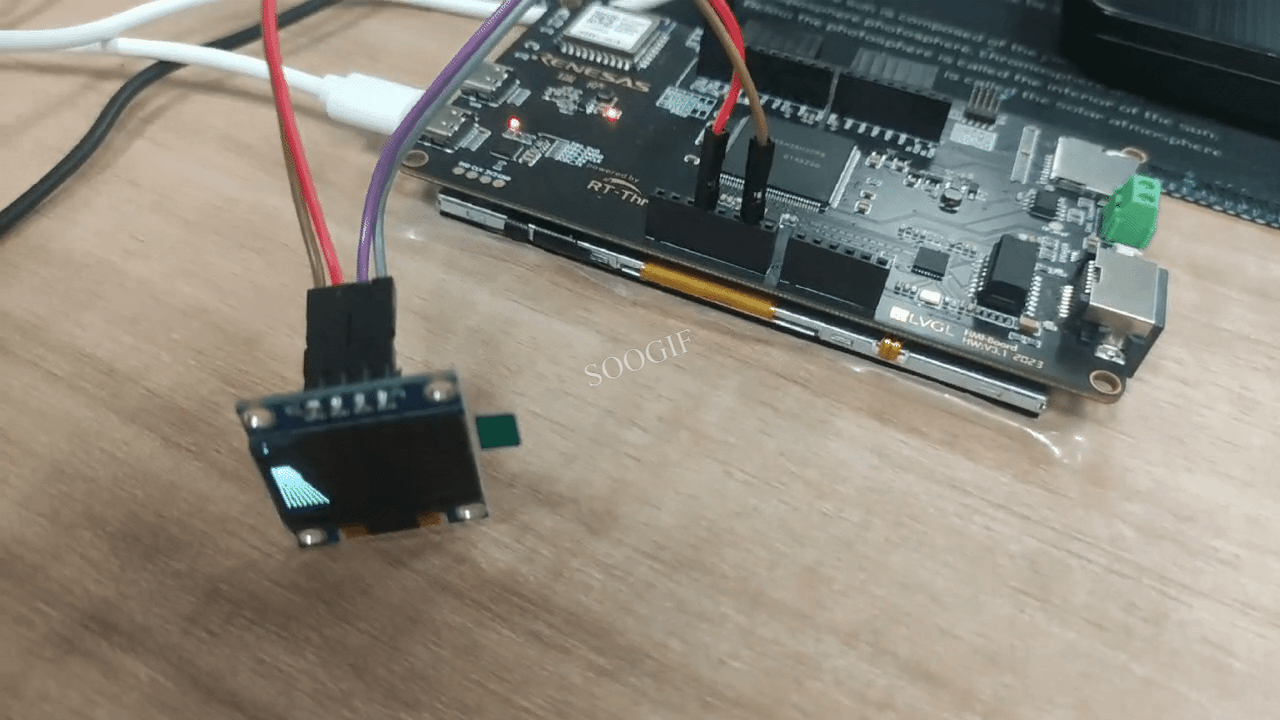
void testdrawbitmap(void) {
display.clearDisplay();
display.drawBitmap(
(display.width() - LOGO_WIDTH ) / 2,
(display.height() - LOGO_HEIGHT) / 2,
logo_bmp, LOGO_WIDTH, LOGO_HEIGHT, 1);
display.display();
delay(1000);
}
#define XPOS 0 // Indexes into the 'icons' array in function below
#define YPOS 1
#define DELTAY 2
void testanimate(const uint8_t *bitmap, uint8_t w, uint8_t h) {
int8_t f, icons[NUMFLAKES][3];
// Initialize 'snowflake' positions
for(f=0; f< NUMFLAKES; f++) {
icons[f][XPOS] = random(1 - LOGO_WIDTH, display.width());
icons[f][YPOS] = -LOGO_HEIGHT;
icons[f][DELTAY] = random(1, 6);
Serial.print(F("x: "));
Serial.print(icons[f][XPOS], DEC);
Serial.print(F(" y: "));
Serial.print(icons[f][YPOS], DEC);
Serial.print(F(" dy: "));
Serial.println(icons[f][DELTAY], DEC);
}
for(;;) { // Loop forever...
display.clearDisplay(); // Clear the display buffer
// Draw each snowflake:
for(f=0; f< NUMFLAKES; f++) {
display.drawBitmap(icons[f][XPOS], icons[f][YPOS], bitmap, w, h, SSD1306_WHITE);
}
display.display(); // Show the display buffer on the screen
delay(200); // Pause for 1/10 second
// Then update coordinates of each flake...
for(f=0; f< NUMFLAKES; f++) {
icons[f][YPOS] += icons[f][DELTAY];
// If snowflake is off the bottom of the screen...
if (icons[f][YPOS] >= display.height()) {
// Reinitialize to a random position, just off the top
icons[f][XPOS] = random(1 - LOGO_WIDTH, display.width());
icons[f][YPOS] = -LOGO_HEIGHT;
icons[f][DELTAY] = random(1, 6);
}
}
}
}
|